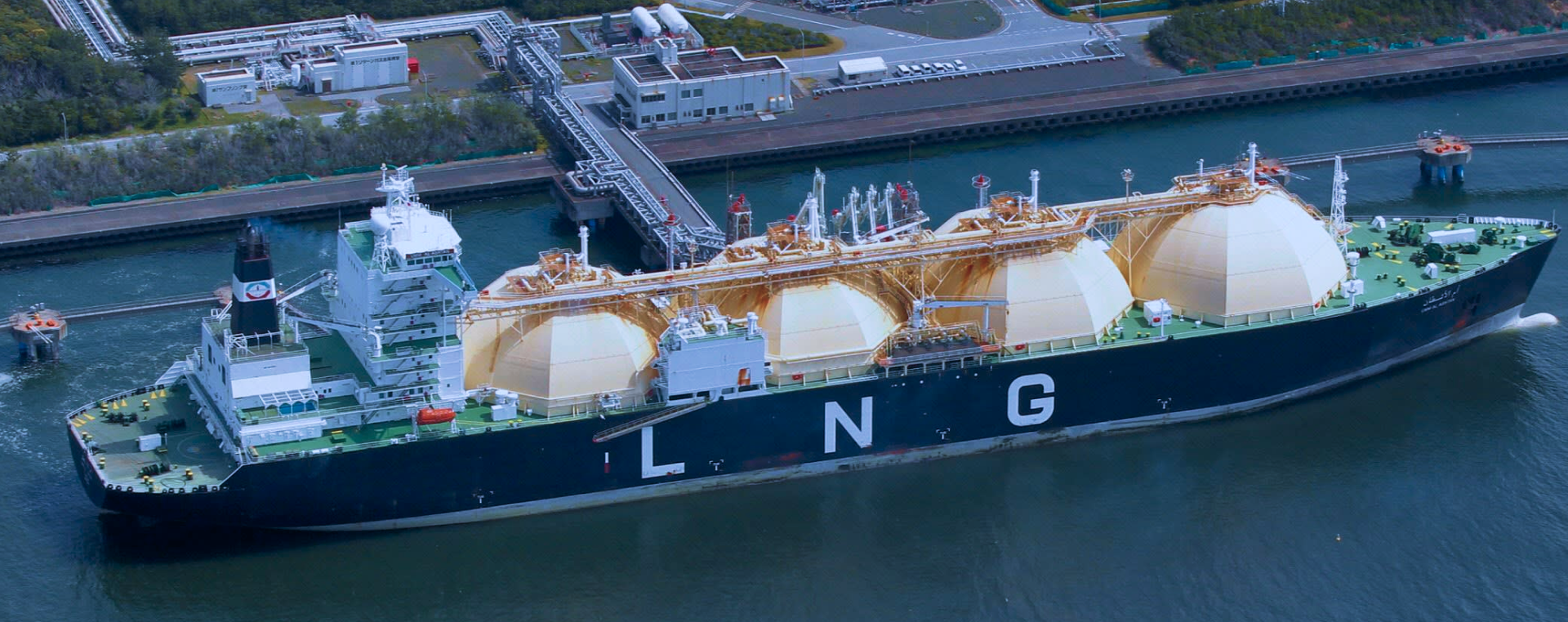
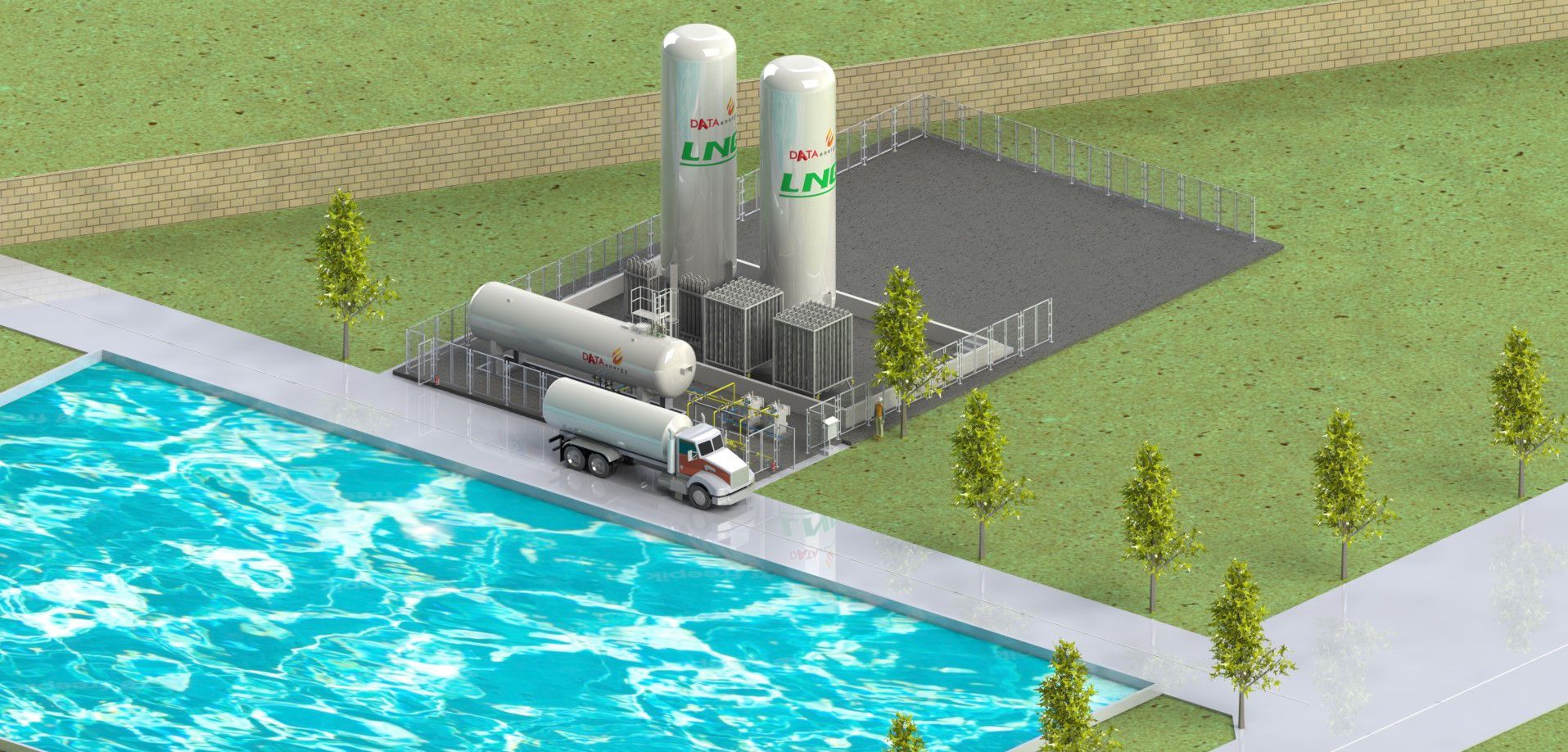
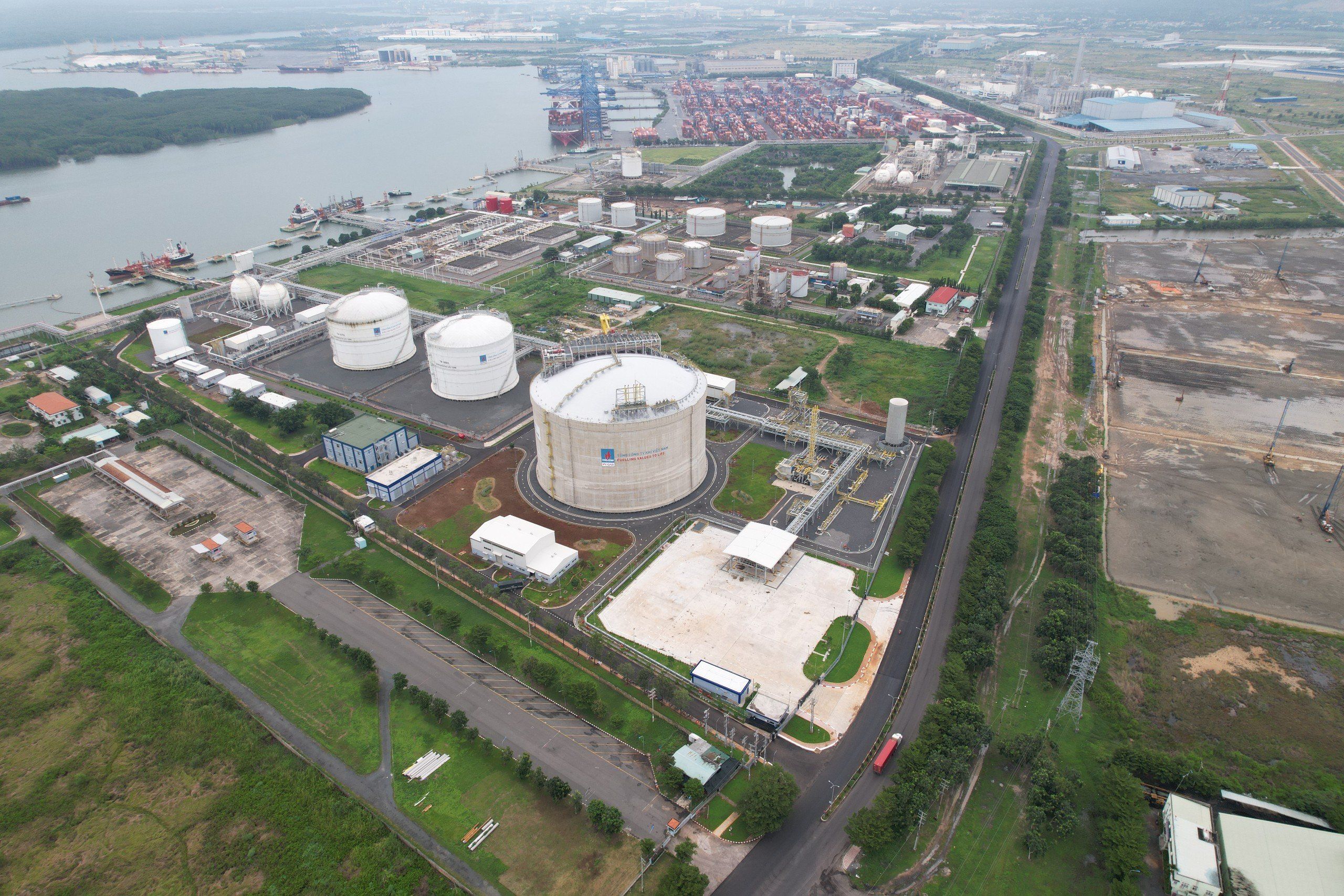
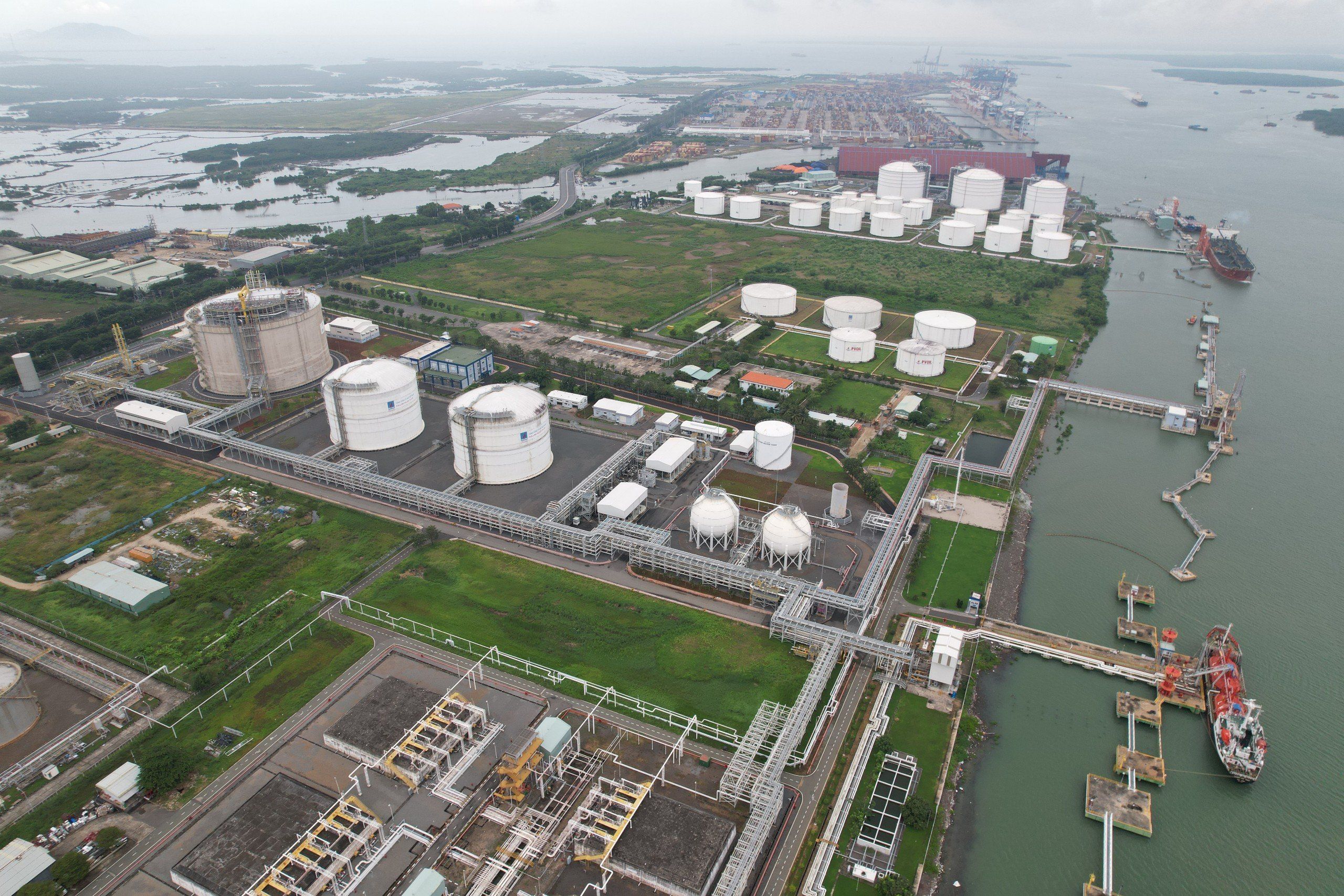
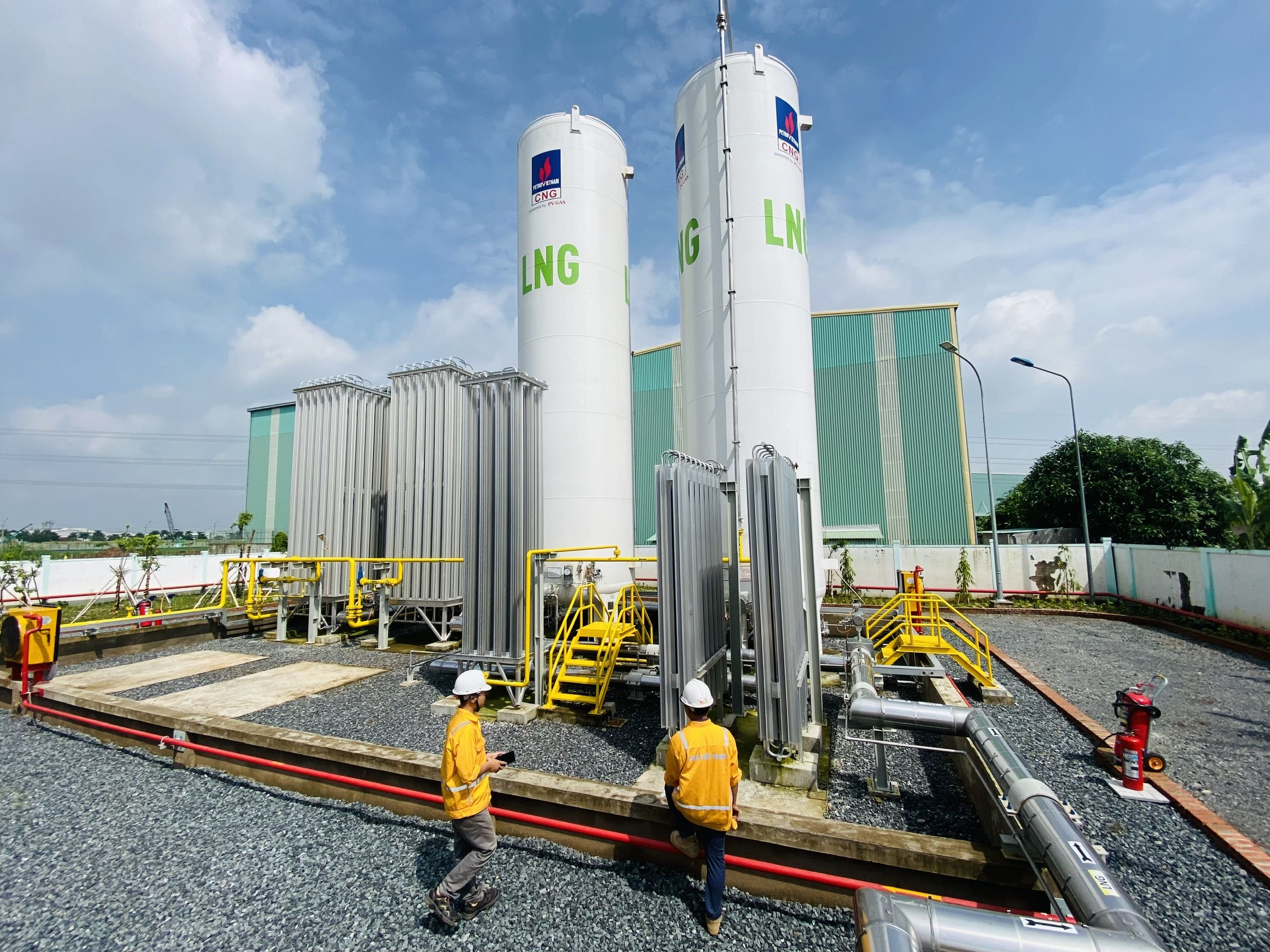
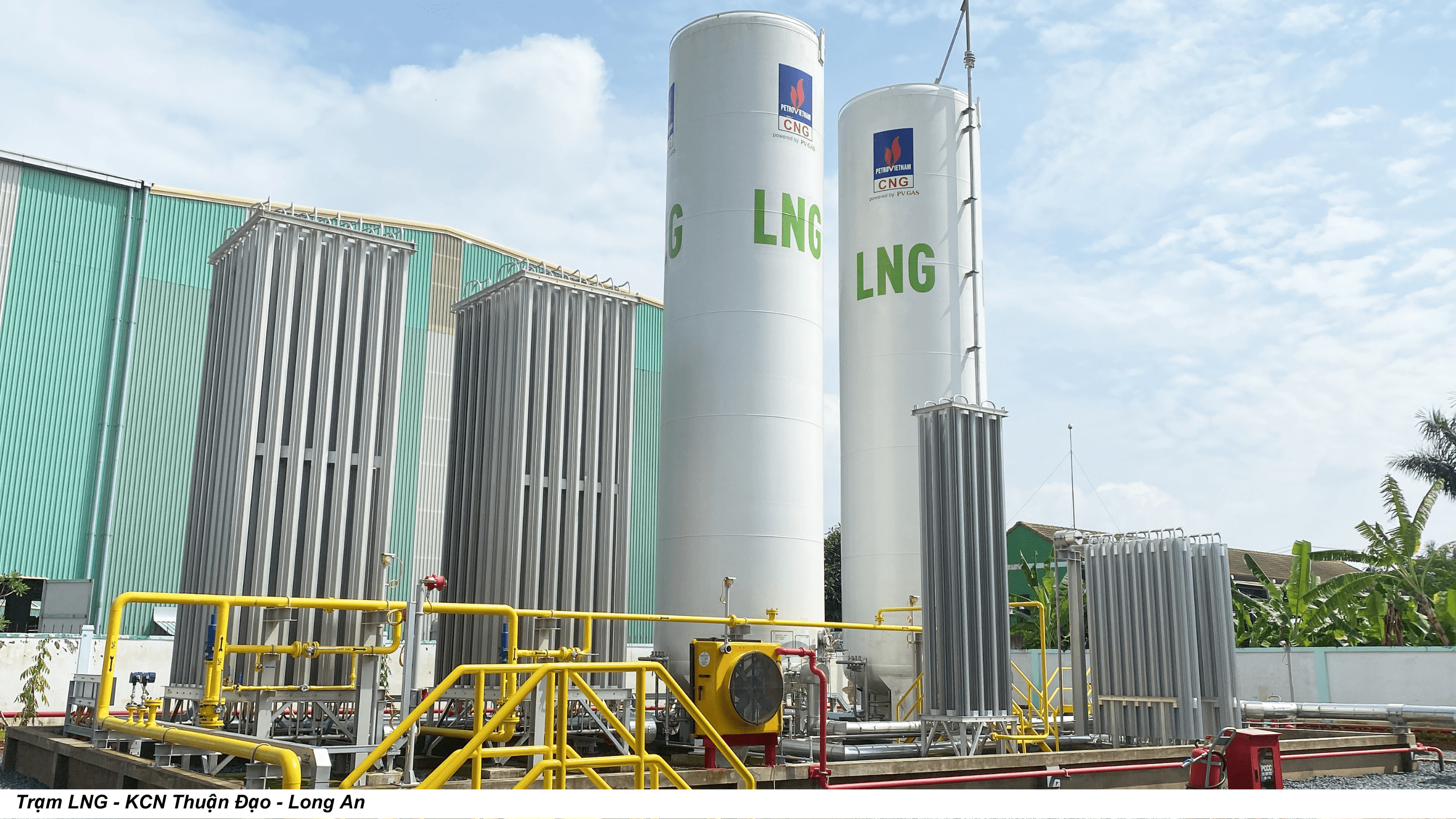
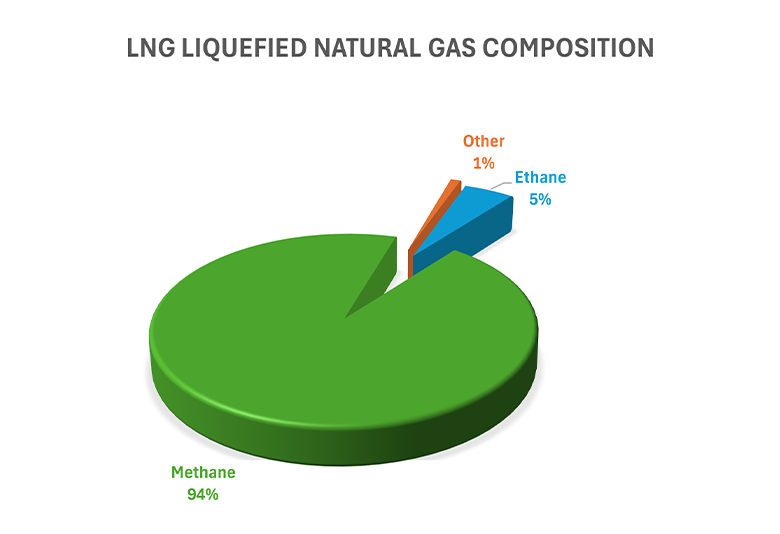
Liquefied Natural Gas (LPG) is a natural gas with the main composition of CH4 - Methane (94.3%), colorless, odorless, non-toxic, cooled at -162ºC to converted to liquid, so the capacity is much higher than CNG (2.4 times).
LNG GAS PRODUCTS
LNG APLLICATION
INDUSTRIAL LNG APPLICATION
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is used in industrial production activities such as: drying, heating, welding, burning, etc. In addition, LNG is also used as fuel for agricultural production such as drying agricultural products, drying, making fertilizer, etc.
OTHER APPLICATION OF LNG
In addition to being used as a fuel in industrial production, LNG is also widely used in other fields such as civil, commercial, and transportation. Liquefied natural gas is also used in power generation and petrochemicals.
practical application

Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is an environmentally friendly gas. The combustion process of LNG emits less CO2, NOx and SO2 (it is estimated that using LNG helps reduce up to 25% of CO2; reduce about 90% of NOx and 98% of SO2, fine dust compared to fossil fuels).

LNG is 600 times smaller in volume than NG, allowing LNG to be transported by ship from the production site to the mainland terminal safely and economically. When it reaches the point of consumption, LNG is simply re-gasified through a special vaporizer.

LNG has a high auto-ignition temperature and a narrow flammability range (5%-15%). This means that if the concentration of LNG in air fluctuates below 5% or above 15%, it will not burn. It is this high ignition temperature and limited flammability range that makes spontaneous ignition or accidental combustion very unlikely.

Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is expected to be competitive in price with heavy fuels such as oil, coal, etc.