COMPARING COMMON TYPES OF BOILERS CURRENTLY IN VIETNAM
12/02/2025
What is a boiler? A boiler, also known as a steam boiler, is a device used to generate steam or hot water by burning various fuels (such as LPG, CNG, coal, oil, etc.) or using other types of energy.
Industrial boilers are important devices widely used in many industrial fields such as electricity generation, steel, rubber, textiles, food processing, and agriculture and aquaculture...
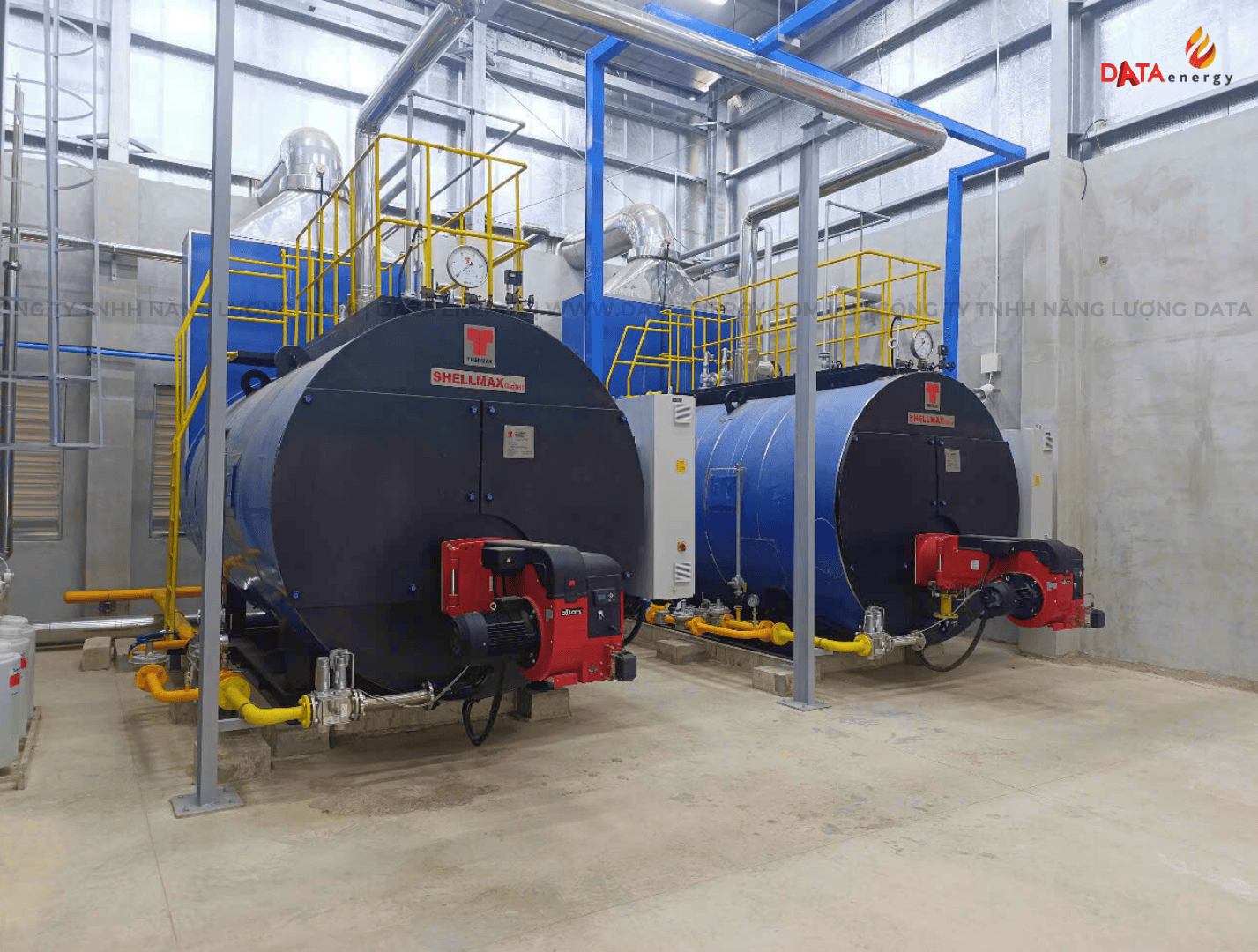

COMPARISON OF COMMON BOILER TYPES TODAY
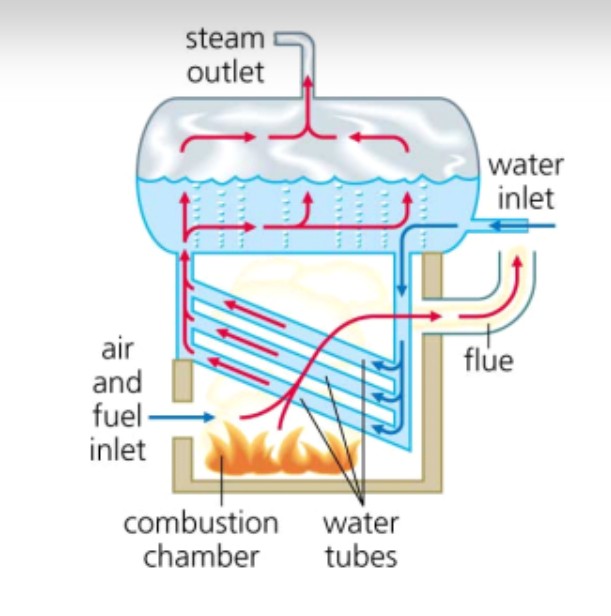
1. Water Tube Boiler:
Operating Principle
- Structure: A water tube boiler consists of many water-carrying tubes, with water contained within these tubes.
- Heating Process: When the boiler is started, fuel (usually coal, oil, LPG gas, LNG, or biomass) is burned in the combustion chamber, and the heat from the combustion process is transferred through the water tubes, heating the water inside.
- Steam Production: When the water reaches its boiling point, steam is generated and accumulated in the steam chamber.
- Pressure Control: The steam is supplied to the industrial system through a pressure regulating valve, ensuring stable and safe operation.
Application
Suitable for factories with high and continuous steam demand such as thermal power plants, food processing, chemical production, and large-scale textile manufacturing.
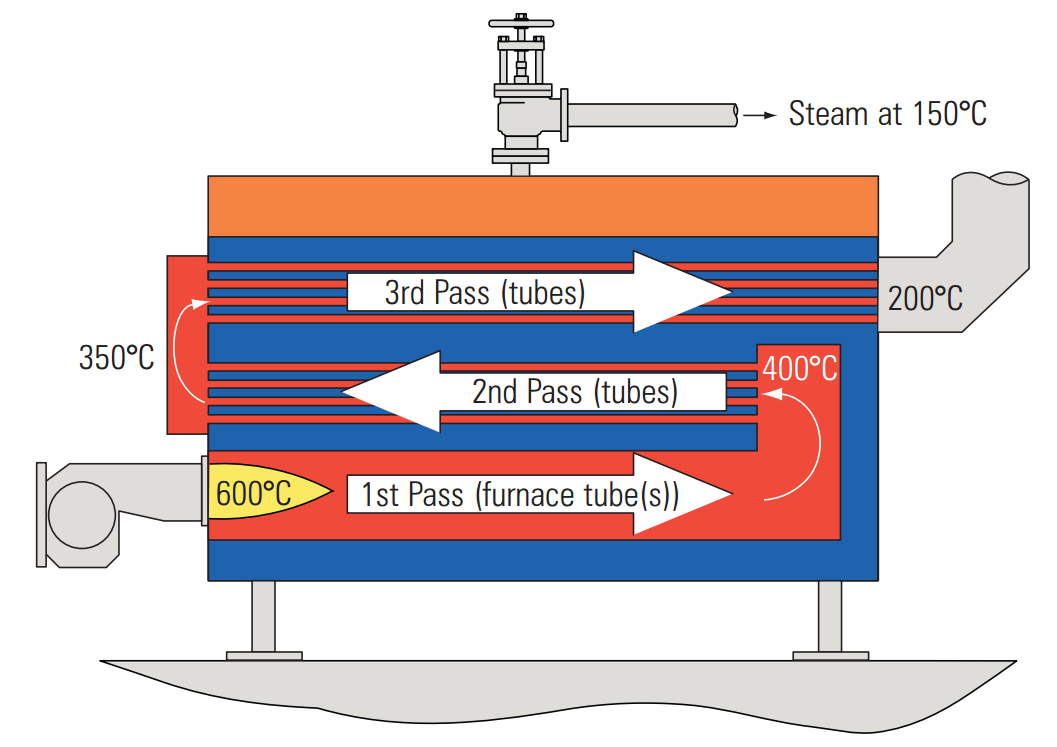
2. Fire-tube boiler:
Operating principle
- Structure: The fire-tube boiler has a cylindrical structure with gas ducts inside.
- Combustion process: Fuel (coal, oil, LPG gas, LNG, or biomass) is burned in the combustion chamber, generating hot gases that pass through the fire tubes, transferring heat to the water outside the tubes.
- Steam production: The water outside the tubes is heated and converted into steam.
- Maintenance and control: The system can be equipped with sensors to monitor temperature and pressure, ensuring safe operation.
Application
Often used in small or medium-sized factories where the demand for steam is not too high, such as in the textile industry, small-scale production, and heating systems.
3. Electric Boiler
Operating Principle
- Structure: The electric boiler uses resistors to heat water.
- Heating Process: When electricity is supplied to the boiler, the resistors generate heat and transfer it to the surrounding water; this process occurs within an optimal time, allowing the water to quickly reach boiling temperature.
- Steam Production: When the water boils, steam is generated and concentrated in the steam chamber, ready to be supplied for industrial applications.
- Temperature Control: Electric boilers are often equipped with automatic controllers to accurately adjust temperature and pressure.

Application
Suitable for small applications where precise temperature control is required and there are no harmful gas emissions, such as in the pharmaceutical and research industries.
COMPARISON TABLE OF POPULAR BOILER TYPES TODAY
| Types of boilers | Operating principle | Advantages | Disadvantages | Price |
| Water tube boiler | Water is heated in tubes, generating steam. |
- High efficiency. - Safer. |
- High investment cost. - Complex maintenance. |
From 1 billion - 5 billion VND |
| Fire tube boiler | Hot smoke from burning fuel passes through water-containing tubes. | - Simple design. - Easy to operate and maintain. |
Lower efficiency compared to water tube boilers. | From 500 million - 2 billion VND |
| Electric boiler | Uses electricity to heat water, generating steam. | - No need for fuel. - Easy to adjust. |
- High operating costs. - Inefficient in large industries. |
From 300 million - 1 billion VND |
In Vietnam, both water tube boilers and fire tube boilers are present in various industries. Water tube boilers are currently becoming more favored in large factories and heavy industries due to performance and energy-saving requirements. Meanwhile, fire tube boilers still play an important role in small and medium applications thanks to their low investment costs.
![]()
DATA ENERGY COMPANY LIMITED (DATA Energy)
- Supply LPG, CNG, LNG.
- Consult, Design, Install Industrial Gas System.
- Invest Gas System (LPG, CNG, LNG) for the factory.