LNG EXPLORATION AND PRODUCTION PROCESS
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas with a main component of methane (CH4) and a mixture of ethane (C2H6). LNG is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and non-corrosive. It is cooled to a liquid state at a temperature of approximately -162°C.
View detail
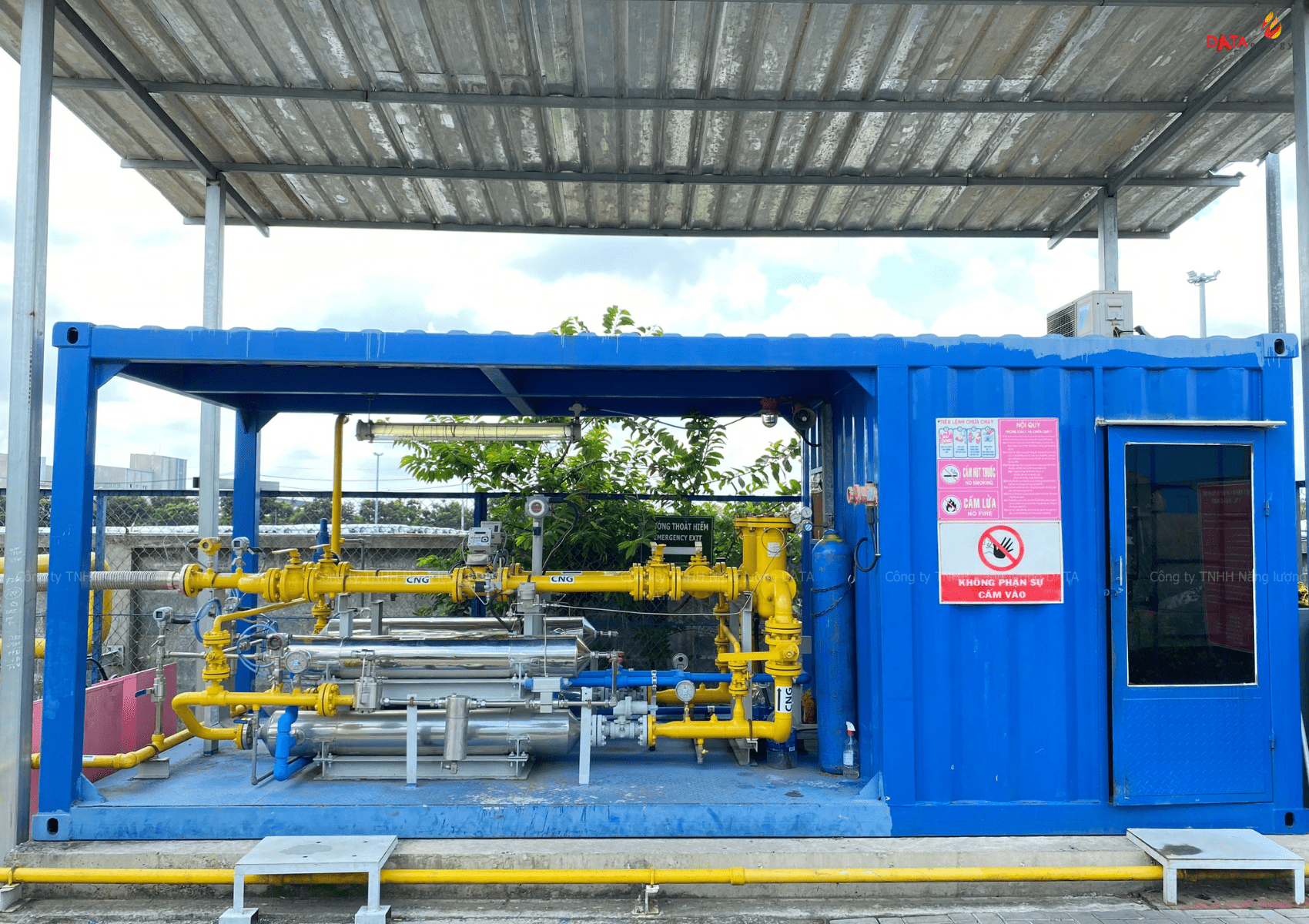

WHAT IS PRU?
PRU (Pressure Reducer Unit) is a part of the compressed natural gas supply system. The main function of PRU is to reduce the gas pressure from high pressure to the appropriate pressure for use.
View detail
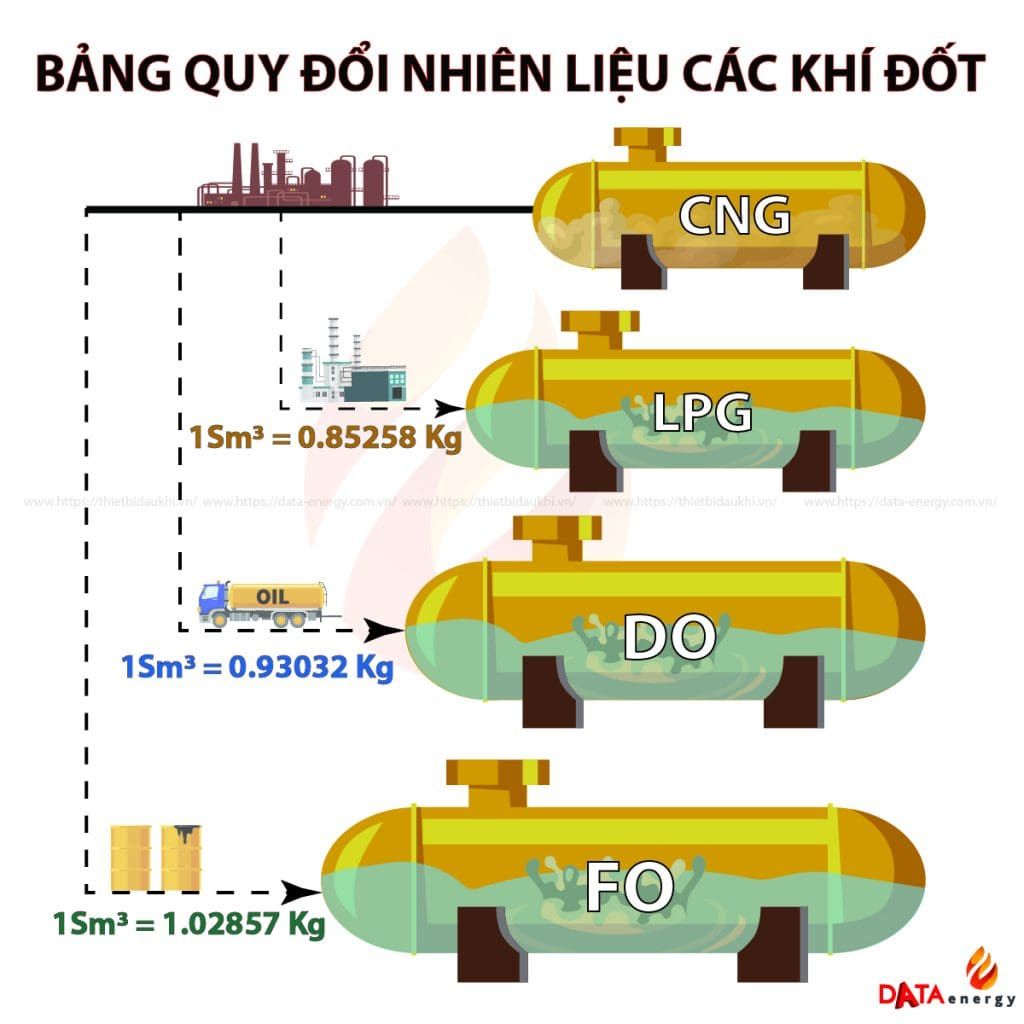
THE FUEL CONVERSION TABLE FOR GAS (CNG, LPG, FO, DO)
Nowadays, gas is a very important fuel with many different uses and performance. So, customers need to understand the fuel conversion table to minimize confusion and make the right choice for their needs and abilities. Below is a table of information on conversion of fuel to gas, everyone can refer to it.
View detail

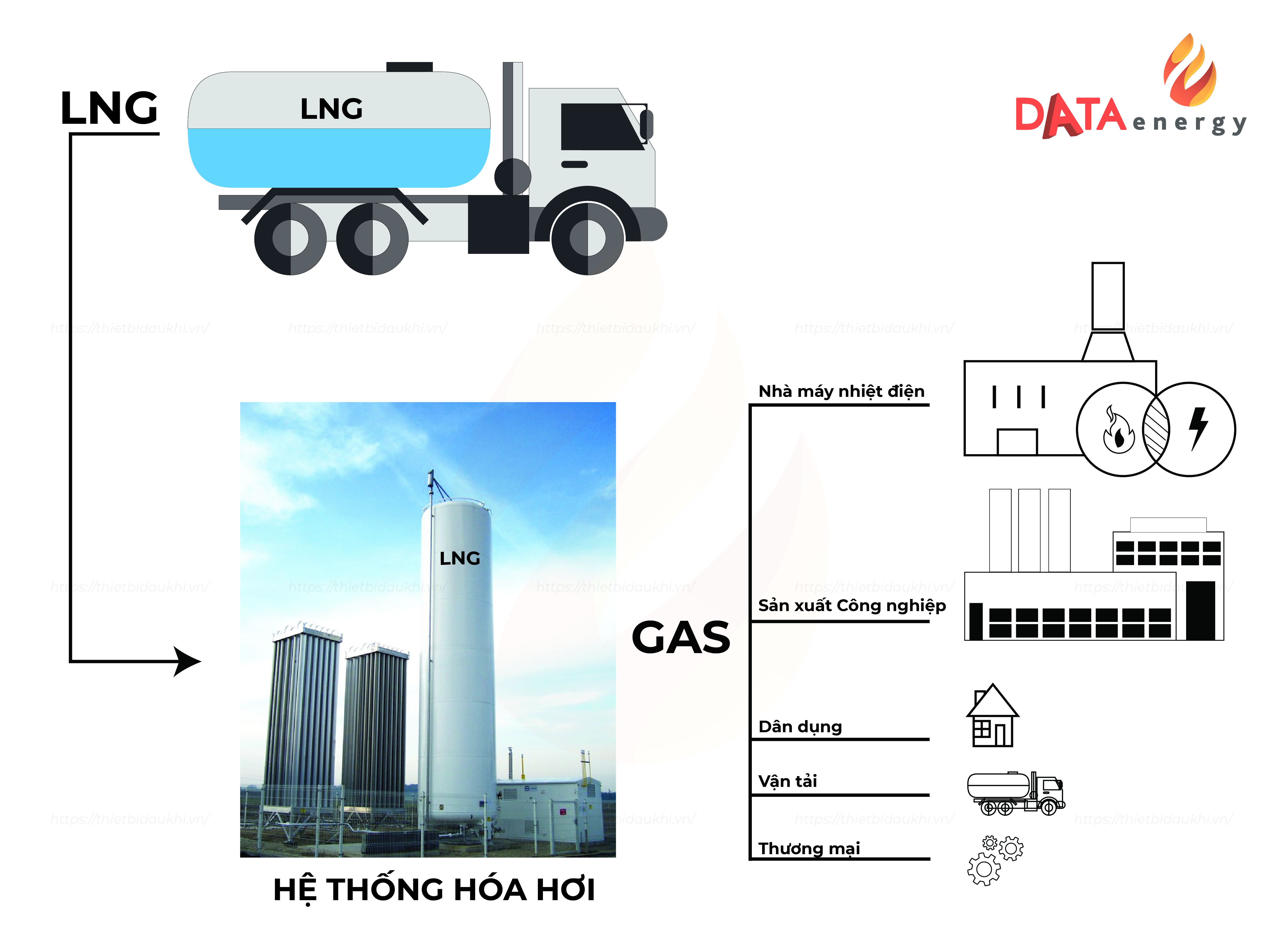
LNG IN INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTION
One of the common applications of liquefied natural gas (LNG) is as fuel for processing in industrial production activities such as heating, drying, burning, etc. Although this is a relatively new type of fuel and is not yet widely used in Vietnam, liquefied natural gas (LNG) is predicted to be a future fuel source in the industrial manufacturing sector due to its advantages.
View detail
SOME COMMON APPLICATIONS OF LNG
Predicted to become a new alternative fuel source in efforts to mitigate the impact of emissions on the environment, Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is being evaluated as a replacement energy source for the present and future globally. Although in developed countries like the US, UK, and Japan, LNG has been widely used and applied for a long time. In the near future, LNG is also promised to become a commonly used fuel in Vietnam with various applications.
View detail

CO2 EMISSION COEFFICIENT FOR FUELS
As the trend of developing green industries becomes increasingly popular in European countries, businesses in Asia are also striving to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in their production and operations. However, in the process of moving towards a "carbon-reduced" industry, businesses need to understand the CO2 emission coefficients to make informed decisions about fuel usage that align with their production circumstances.
View detail

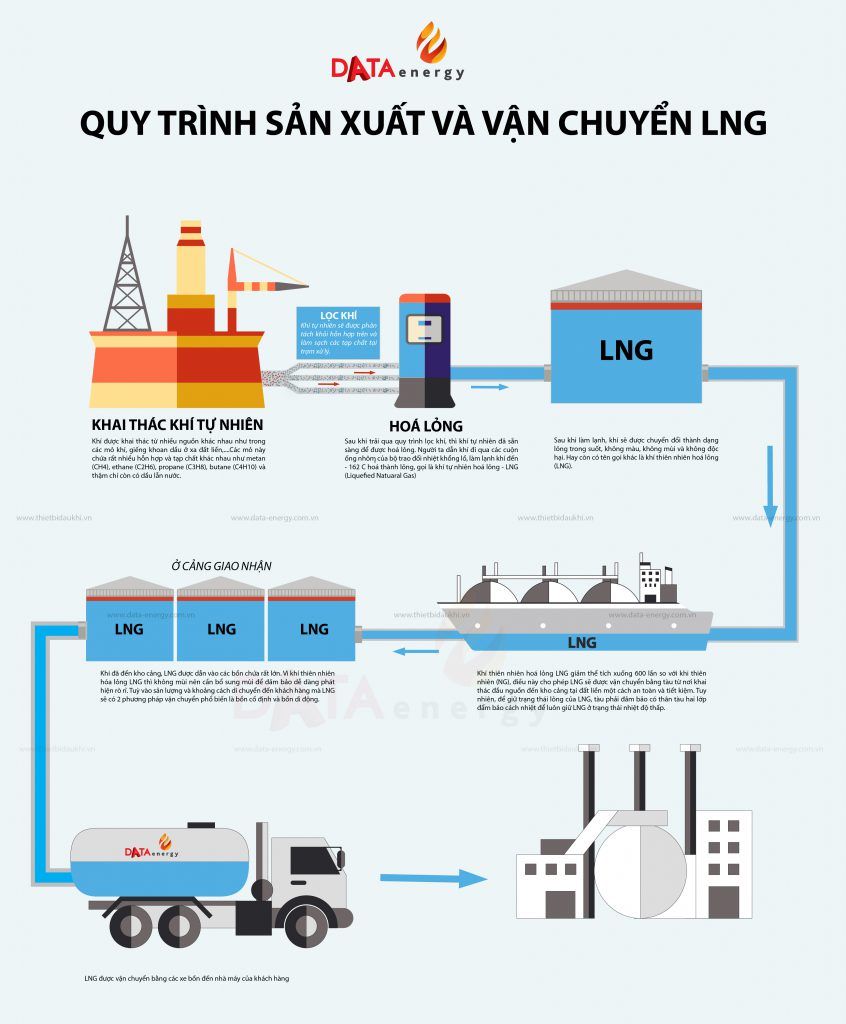
WHAT IS LIQUEFIED NATURAL GAS (LNG)?
Natural gas is extracted from various sources such as gas fields and oil wells far offshore. These sources contain a mixture of different impurities, including methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10), and even oil and water. The natural gas will be separated from these mixtures and purified at a gas processing station.
View detail







