WHAT IS CALORIFIC VALUE? CALORIFIC VALUE OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF FUEL GASES
06/01/2025
Calorific value (also known as heat of combustion) is a unit of measurement for the amount of heat generated when completely burning (1kg) of solid or liquid fuel or (1m3) of gaseous fuel.
Calorific value is usually measured in units of Kcal/kg or Cal/g.

In the energy and industrial sectors, the calorific value of a fuel is classified based on the amount of heat generated when that fuel is burned. We can categorize calorific value into two types: Higher Heating Value (HHV) and Lower Heating Value (LHV).
High calorific value: This refers to the large amount of heat generated when a fuel is burned. This allows for the production of a large amount of heat without using an excessive amount of fuel. With a high calorific value, boilers and furnaces can maximize the energy generated from the fuel and improve efficiency.
Low calorific value: This refers to a lower amount of heat generated when fuel is burned. With a low calorific value, the efficiency of boilers and furnaces will decrease, leading to inefficient fuel usage.
CALORIFIC VALUE OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF GAS.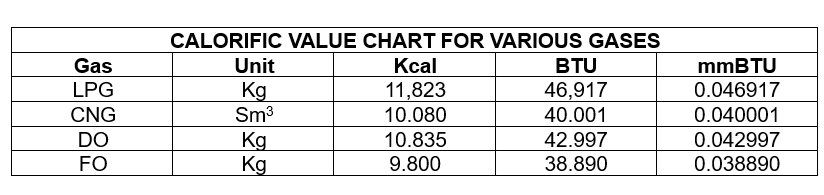 Note:
Note:
1. BTU (British Thermal Unit): A unit of heat energy in the British system.
2. Sm3 (Standard cubic metre): 1 cubic meter of CNG at standard conditions (temperature 15oC, pressure 1 at).
3. mmBTU: One million BTU.
1kcal = 3.968321 BTU.
The importance of calorific value:
Calorific value is an important indicator. By applying calorific value, we can compare and evaluate the performance of different types of fuels/gases. This helps us choose the optimal fuel to achieve the highest utilization efficiency and best productivity in customer production processes.
![]()
DATA ENERGY COMPANY LIMITED (DATA Energy)
- Supply LPG, CNG, LNG.
- Consult, Design, Install Industrial Gas System.
- Invest Gas System (LPG, CNG, LNG) for the factory.